- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Occupational exposure limit values
- Climate Change and Occupational Safety
- List of CMR substances
- Electromagnetic fields
- Ergonomics
- Industrial Security
- Collaborative robots
- Noise
- Nanoparticles at the workplace
- Optical Radiation
- REACH
- Reference materials
- Proficiency testing
- Vibration
- Virtual reality
- Work 4.0
Natural optical radiation

Source: Günter Albers - stock.adobe.com
The main source of natural optical radiation is the sun. The greatest hazards of solar radiation are presented by its ultraviolet (UV) component. This can cause both acute damage (sunburn) and severe, chronic consequences for the eyes (cataracts) and skin (skin cancer). The UV range is in the short-wave region of the solar spectrum and is divided into three sub-ranges:
UV-A: 400-315 nm
UV-B: 315-280 nm
UV-C: 280-100 nm
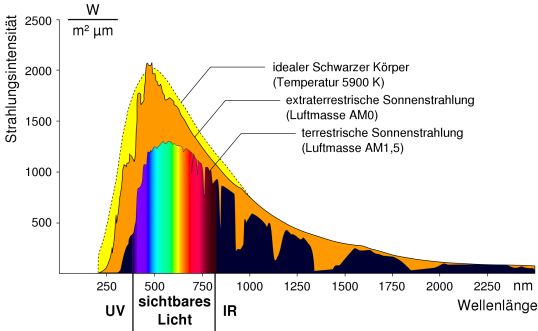
Intensity of the solar radiation at the earth’s surface (terrestrial solar radiation) compared to the radiation intensity above the atmosphere (extraterrestrial solar radiation) and the spectrum of an ideal black body (at 5,900 Kelvin), with definition of the wavelength ranges
Source: Degreen
Since always, people have worked outdoors in construction, agriculture and other areas and have been exposed there to ultraviolet radiation from the sun. Outdoor workers face an elevated risk of skin cancer. This risk can, however, be reduced effectively by simple protective measures.
Owing to the demographic trend in the population and changes in the environment caused by meteorological changes due to climate change, a drastic increase in cases of skin cancer is forecast. The level of actual risk to certain occupational groups can be estimated only by means of task-specific exposure data. Not until the launch of the GENESIS-UV measurement project, however, was such measurement data available. Detailed observations on UV exposure at work and during leisure time were gathered in the course of the GENESIS-UV project. The resulting body of data can now be used for drawing valuable conclusions for the prevention of occupational skin cancer.
Information on the GENESIS-UV project: measurement of occupational UV exposure
Information on the GENESIS-UV project: Leisure time UV exposure
Contact:
Ergonomics, Physical environmental factors
Tel: +49 30 13001-3470Fax: +49 30 13001-38001